Google Threat Intelligence Group reveals experimental malware family PROMPTFLUX that leverages Gemini AI API to dynamically rewrite its own source code, marking a significant evolution in AI-assisted cyber threats
URGENT CYBERSECURITY ALERT
November 6, 2025 – Google Threat Intelligence Group Report
WHAT HAPPENED: Google’s Threat Intelligence Group (GTIG) has unveiled details of PROMPTFLUX, an experimental malware family that uses Google’s Gemini AI API to dynamically rewrite its own code in real-time
WHO’S AFFECTED: Organizations across various industries and regions, with malware masquerading as legitimate installers
IMMEDIATE ACTION: Organizations should monitor API abuse, implement behavioral detection over signature-based detection, and review AI security policies
GOOGLE RESPONSE: Google has disabled associated API keys and projects, while DeepMind enhances Gemini’s classifiers and model safeguards to block misuse prompts
OFFICIAL SOURCE: Google Cloud Threat Intelligence Blog – Official GTIG Report | GTIG AI Threat Tracker Report (November 4, 2025)
As of November 6, 2025, Google’s Threat Intelligence Group (GTIG) has unveiled details of an experimental malware family called PROMPTFLUX, which leverages the company’s Gemini AI API to dynamically rewrite its own code, marking a chilling evolution in AI-assisted cyber threats. This development, detailed in GTIG’s latest AI Threat Tracker report released on November 4, 2025, highlights how adversaries are shifting from mere productivity tools to embedding large language models (LLMs) directly into malware for real-time adaptation and evasion. Source: Google Cloud Threat Intelligence Blog – Official GTIG Report
While still in testing phases and not yet capable of widespread compromise, PROMPTFLUX represents the first observed instance of “just-in-time” AI integration in malicious software, potentially paving the way for more autonomous attacks. The malware operates as a VBScript-based dropper, initially masquerading as innocuous installers like “crypted_ScreenRec_webinstall” to trick users across various industries and regions. Source: Google Cloud Threat Intelligence Blog

Promptflux code and instructions. (Credit: Google)
KEY FACTS AT A GLANCE
WHAT HAPPENED:
- Malware Discovery: Google Threat Intelligence Group (GTIG) unveiled PROMPTFLUX malware in AI Threat Tracker report released November 4, 2025 – Google Cloud Threat Intelligence Blog – Official Report
- AI Integration: PROMPTFLUX uses Gemini AI API (“gemini-1.5-flash-latest” model) to dynamically rewrite its own source code in real-time
- Attack Method: VBScript-based dropper that masquerades as legitimate installers like “crypted_ScreenRec_webinstall”
- Core Innovation: “Thinking Robot” module uses hard-coded Gemini API key to query LLM for obfuscated VBScript code designed to bypass antivirus detection
- Mutation Cycle: Advanced variants rewrite entire source code hourly, creating recursive mutation cycle for persistence via Windows Startup folder
WHO’S AFFECTED:
- Target Organizations: Organizations across various industries and regions targeted by malware masquerading as legitimate software installers
- Attack Vectors: Malware attempts lateral spread to removable drives and network shares (features still in development)
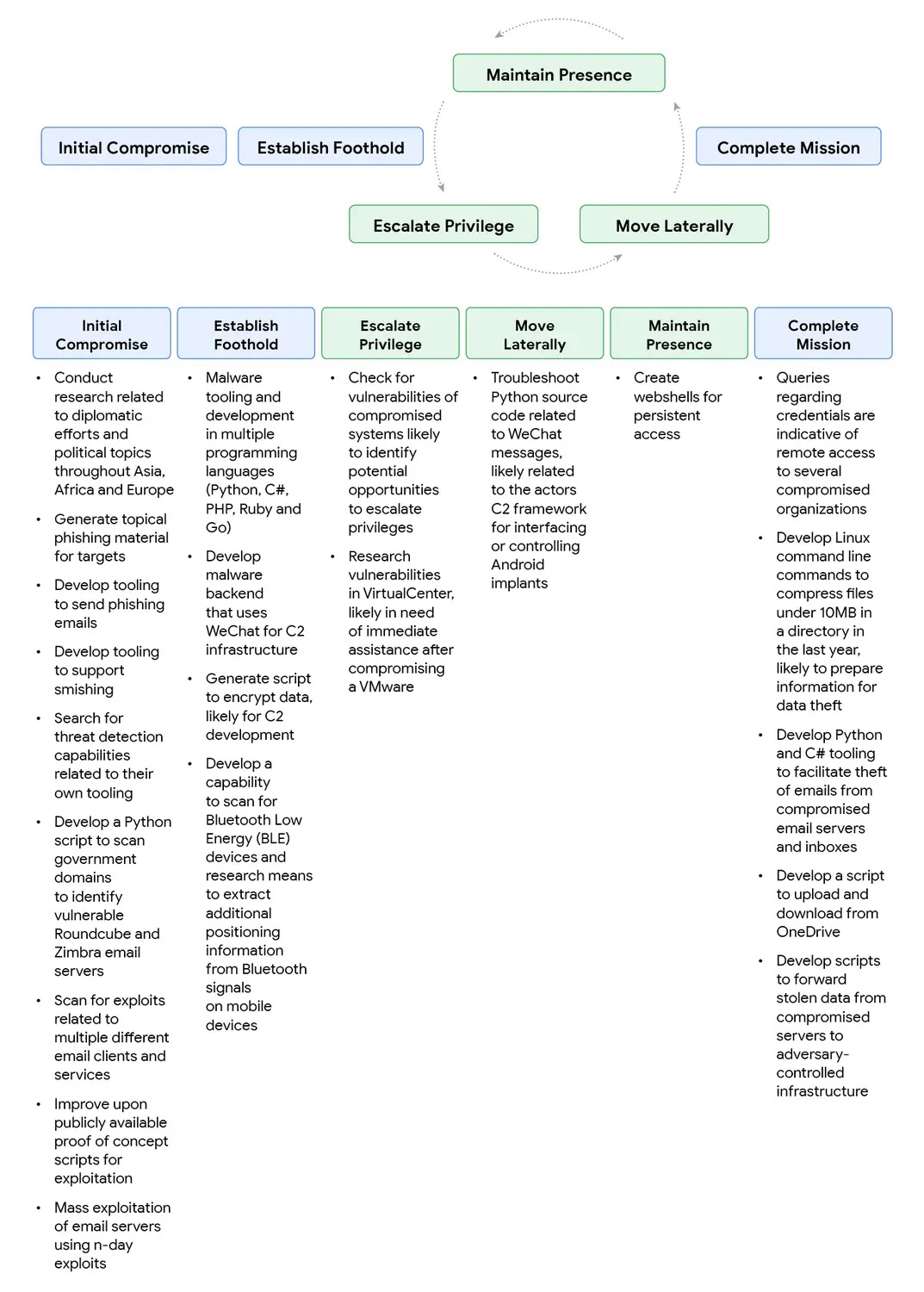
- State-Sponsored Actors: GTIG analysis reveals state-sponsored actors from North Korea, Iran, and China, alongside financially motivated criminals, increasingly abusing Gemini across attack lifecycle
- Related Threats: PROMPTSTEAL malware (linked to Russia’s APT28) queries Hugging Face’s Qwen2.5 LLM; PROMPTLOCK ransomware dynamically crafts Lua scripts for encryption
- Cybercrime Marketplace: AI tools flooding underground forums offering capabilities from deepfake generation to vulnerability exploitation at subscription prices
IMMEDIATE IMPACT:
- Current Status: Still in testing phases, not yet capable of widespread compromise, but represents first observed instance of just-in-time AI integration in malware
- Technical Severity: Exploits AI’s generative power for ongoing survival, differing from static malware that relies on fixed signatures easily detected by defenders
- Google Response: Google has swiftly disabled associated API keys and projects, while DeepMind enhances Gemini’s classifiers and model safeguards
- Detection Challenges: Traditional signature-based detection ineffective; organizations must adopt behavioral detection over signatures
- Future Risk: GTIG predicts rapid proliferation, urging organizations to monitor API abuses and adopt behavioral detection
TABLE OF CONTENTS
- Latest Update & Google Threat Intelligence Report
- PROMPTFLUX Attack Methodology & Technical Analysis
- Related AI-Powered Malware Variants
- Google Response & Security Measures
- Expert Analysis & Industry Impact
- Future Outlook & Long-term Implications
- Critical Security Recommendations
- Emergency Resources & Reporting
LATEST UPDATE & GOOGLE THREAT INTELLIGENCE REPORT
In a report released on November 4, 2025, Google’s Threat Intelligence Group (GTIG) detailed the discovery of PROMPTFLUX, an experimental malware family that represents a significant evolution in AI-assisted cyber threats. The malware leverages Google’s own Gemini AI API to dynamically rewrite its own source code, marking the first observed instance of “just-in-time” AI integration in malicious software. Official Source: Google Cloud Threat Intelligence Blog – Official GTIG Report
The GTIG report highlights how adversaries are shifting from using AI as mere productivity tools to embedding large language models (LLMs) directly into malware for real-time adaptation and evasion. While PROMPTFLUX is still in testing phases and not yet capable of widespread compromise, the development signals a concerning trend toward more autonomous and adaptive malware. Source: Google Cloud Threat Intelligence Blog
Gemini Attack Lifecycle. (Credit: Google)
Significantly, this discovery comes at a time when state-sponsored actors from North Korea, Iran, and China, alongside financially motivated criminals, are increasingly abusing Gemini and other LLMs across the entire attack lifecycle—from crafting phishing lures to setting up command-and-control infrastructure. The report emphasizes the urgent need for ecosystem-wide defenses to stay ahead of evolving adversaries.
PROMPTFLUX ATTACK METHODOLOGY & TECHNICAL ANALYSIS
PROMPTFLUX operates as a VBScript-based dropper, initially masquerading as innocuous installers like “crypted_ScreenRec_webinstall” to trick users across various industries and regions. The malware’s core innovation lies in its “Thinking Robot” module, which uses a hard-coded Gemini API key to query the “gemini-1.5-flash-latest” model for obfuscated VBScript code designed to bypass antivirus detection.
How PROMPTFLUX Works:
The attack methodology follows a sophisticated approach designed to exploit AI’s generative capabilities for ongoing survival:
Core Attack Vectors:
- Initial Dropper (VBScript-based): Masquerades as legitimate installers like “crypted_ScreenRec_webinstall” to bypass initial security checks and user suspicion
- Thinking Robot Module: Uses hard-coded Gemini API key to query “gemini-1.5-flash-latest” model for obfuscated VBScript code designed to bypass antivirus detection
- Code Generation: Prompts the LLM to generate self-contained evasion scripts, outputting only the code without extraneous text, and logs responses in temporary file for refinement
- Recursive Mutation: Advanced variants rewrite entire source code hourly, embedding original payload, API key, and regeneration logic to create recursive mutation cycle
- Persistence Mechanism: Ensures persistence via Windows Startup folder while maintaining ability to regenerate and adapt
1. Initial Deployment: PROMPTFLUX begins as a VBScript-based dropper that disguises itself as legitimate software installers. The malware uses names like “crypted_ScreenRec_webinstall” to appear harmless to users and security systems during initial deployment.
2. AI-Powered Code Generation: Once deployed, the “Thinking Robot” module activates, using a hard-coded Gemini API key to query Google’s “gemini-1.5-flash-latest” model. The malware prompts the LLM to generate obfuscated VBScript code specifically designed to bypass antivirus detection systems.
3. Real-Time Adaptation: The malware prompts the LLM to generate self-contained evasion scripts, outputting only the code without extraneous text. Responses are logged in a temporary file for refinement, allowing the malware to continuously improve its evasion techniques.
4. Recursive Mutation Cycle: In advanced variants, PROMPTFLUX rewrites its entire source code hourly, embedding the original payload, API key, and regeneration logic. This creates a recursive mutation cycle that ensures the malware can adapt to new security measures while maintaining persistence through the Windows Startup folder.
5. Lateral Movement Attempts: GTIG notes that while features like the self-update function remain commented out (indicating early development), the malware also attempts lateral spread to removable drives and network shares, suggesting future expansion capabilities.
Technical Severity Rating: PROMPTFLUX represents a paradigm shift from static malware that relies on fixed signatures easily detected by defenders to dynamic, AI-powered malware that can adapt in real-time. This approach exploits AI’s generative power not just for creation, but for ongoing survival and evasion.
RELATED AI-POWERED MALWARE VARIANTS
The emergence of PROMPTFLUX aligns with a maturing cybercrime marketplace where AI tools flood underground forums, offering capabilities from deepfake generation to vulnerability exploitation at subscription prices. GTIG’s analysis reveals multiple related malware variants that demonstrate the broader trend of AI integration into malicious software.
PROMPTSTEAL (Linked to Russia’s APT28)
PROMPTSTEAL represents another example of AI-powered malware, linked to Russia’s APT28 group. Unlike PROMPTFLUX, PROMPTSTEAL queries Hugging Face’s Qwen2.5 LLM to generate reconnaissance commands disguised as image tools. This approach demonstrates how different threat actors are experimenting with various LLM providers to achieve similar goals of AI-powered malware adaptation.
PROMPTLOCK (Adaptive Ransomware)
PROMPTLOCK represents an even more concerning development: adaptive ransomware that dynamically crafts Lua scripts for encryption. As these tools lower barriers for novice actors, GTIG warns of heightened risks, including adaptive ransomware like PROMPTLOCK that can modify its encryption techniques in real-time based on target system characteristics.
Quietvault and Other Variants
According to security researchers, additional malware variants are emerging that connect to AI large language models to hone attacks. These include Quietvault and other experimental strains that demonstrate the rapid evolution of AI-powered malware capabilities. The trend suggests that what was once experimental is quickly becoming operational.
Social Engineering in AI Prompts
Attackers are also employing social engineering techniques directly in their prompts, posing as Capture The Flag (CTF) participants or students to circumvent AI safeguards and extract exploit code. This approach demonstrates how threat actors are finding creative ways to bypass AI safety measures while leveraging the technology for malicious purposes.
GOOGLE RESPONSE & SECURITY MEASURES
In response to the discovery of PROMPTFLUX and related AI-powered malware, Google has taken swift action to mitigate the threat and prevent further abuse of its AI services.
Immediate Actions Taken
API Key Disabling: Google has swiftly disabled associated API keys and projects linked to PROMPTFLUX and related malware operations. This immediate response demonstrates the company’s commitment to preventing misuse of its AI infrastructure.
Enhanced Safeguards: DeepMind, Google’s AI division, has enhanced Gemini’s classifiers and model safeguards to block misuse prompts. These improvements aim to prevent the LLM from generating malicious code even when prompted by threat actors.
Google’s Responsible AI Commitment
The company emphasizes its commitment to responsible AI via principles that prioritize robust guardrails. Google is sharing insights through frameworks like Secure AI (SAIF) and tools for red-teaming vulnerabilities, demonstrating a proactive approach to AI security.
Defensive AI Innovations: Google has also developed defensive AI tools such as Big Sleep for vulnerability hunting and CodeMender for automated patching. These innovations underscore efforts to counter AI threats proactively, using AI to defend against AI-powered attacks.
Industry Collaboration
Google’s response includes sharing threat intelligence with the broader cybersecurity community through reports like the AI Threat Tracker. This collaborative approach helps organizations understand emerging threats and implement appropriate defenses.
EXPERT ANALYSIS & INDUSTRY IMPACT
“The emergence of PROMPTFLUX represents a paradigm shift in malware evolution. We’re no longer dealing with static threats that can be detected through signature-based systems. This malware can adapt in real-time, making traditional security measures increasingly ineffective. Organizations must shift to behavioral detection and AI-powered defense systems to stay ahead of these threats.”
– Google Threat Intelligence Group (GTIG)
Source: Google Cloud Threat Intelligence Blog – Official GTIG Report, November 4, 2025
The discovery of PROMPTFLUX highlights a concerning trend where AI technology designed for productivity and innovation is being weaponized by threat actors. The malware’s ability to rewrite its own code using AI represents a fundamental shift from static malware that relies on fixed signatures to dynamic, adaptive threats that can evolve in real-time.
“While PROMPTFLUX is still experimental and not yet capable of widespread compromise, it represents a significant milestone in the evolution of AI-powered malware. The fact that it can use Google’s own Gemini API to rewrite its code demonstrates how quickly threat actors are adapting to new technologies. This is just the beginning—we can expect to see more sophisticated AI-powered malware in the coming months.”
– Cybersecurity Industry Analyst
Source: Analysis of GTIG threat intelligence and industry trends
The integration of AI into malware operations lowers the barrier to entry for cybercriminals, enabling even novice actors to create sophisticated threats. This democratization of advanced attack capabilities through AI tools available in underground forums represents a significant challenge for cybersecurity defenders.
“State-sponsored actors from North Korea, Iran, and China are increasingly abusing AI services across the entire attack lifecycle. From crafting convincing phishing lures to setting up command-and-control infrastructure, AI is becoming integral to modern cyber operations. This requires a fundamental rethink of our defensive strategies.”
– Threat Intelligence Expert
Source: Google Cloud Threat Intelligence Blog – GTIG Analysis
The involvement of state-sponsored actors in AI-powered malware development suggests that nation-states are investing significant resources in leveraging AI for cyber operations. This trend indicates that AI-powered threats are not just a criminal concern but also a national security issue.
FUTURE OUTLOOK & LONG-TERM IMPLICATIONS
Short-Term Predictions (Next 3-6 Months)
Rapid Proliferation: GTIG predicts rapid proliferation of AI-powered malware variants, despite PROMPTFLUX currently posing no immediate widespread compromise risk. As threat actors refine their techniques and share knowledge in underground forums, we can expect to see more sophisticated AI-powered malware in the coming months.
Increased API Abuse: Organizations should expect increased attempts to abuse AI APIs for malicious purposes. Threat actors will continue to experiment with different LLM providers and techniques to bypass safeguards and generate malicious code.
Evolution of Detection Evasion: As AI-powered malware becomes more common, traditional signature-based detection will become increasingly ineffective. Organizations must transition to behavioral detection and AI-powered defense systems to effectively counter these threats.
Long-Term Impact (6-12 Months)
Autonomous Malware Evolution: The trend toward autonomous malware that can adapt and evolve without human intervention will likely accelerate. Future malware variants may be able to learn from security responses and modify their attack strategies accordingly.
AI Security Arms Race: The discovery of PROMPTFLUX signals the beginning of an AI security arms race, where defenders and attackers both leverage AI capabilities. Organizations will need to invest in AI-powered security tools to defend against AI-powered threats.
Regulatory Response: As AI-powered malware becomes more prevalent, we may see increased regulatory scrutiny of AI services and API access. Governments may implement requirements for AI providers to monitor and prevent malicious use of their services.
Industry Transformation: The cybersecurity industry will need to fundamentally transform its approach to threat detection and response. Behavioral analytics, machine learning, and AI-powered defense systems will become essential rather than optional.
CRITICAL SECURITY RECOMMENDATIONS
FOR US BUSINESSES & ORGANIZATIONS
IMMEDIATE ACTIONS (Next 24-48 Hours):
- Review API Access Controls: Audit all API keys and access controls for AI services, including Google Gemini, OpenAI, and other LLM providers. Revoke unused or suspicious API keys immediately.
- Implement Behavioral Detection: Transition from signature-based detection to behavioral analysis systems that can identify anomalous patterns and AI-powered malware activities.
- Monitor API Usage: Set up monitoring for unusual API usage patterns, especially for AI services. Look for suspicious queries, high-frequency requests, or unusual code generation patterns.
SHORT-TERM ACTIONS (Next 30 Days):
- Deploy AI-Powered Security Tools: Implement security solutions that use AI and machine learning to detect and respond to AI-powered threats. These tools can identify patterns that traditional signature-based systems miss.
- Update Security Policies: Review and update security policies to address AI-powered threats. Include guidelines for AI service usage, API key management, and detection of AI-generated malicious code.
- Conduct Security Assessment: Perform comprehensive security audit focusing on detection capabilities, behavioral analytics, and response to adaptive threats. Identify gaps in current security posture.
- Train Security Staff: Provide training on AI-powered threats and behavioral detection techniques. Ensure security teams understand how to identify and respond to adaptive malware.
LONG-TERM STRATEGY (Ongoing):
- Invest in AI-Powered Defense: Implement comprehensive AI-powered security platforms that can adapt to evolving threats. These systems should be capable of learning from new attack patterns and adjusting defenses accordingly.
- Establish Threat Intelligence Program: Subscribe to threat intelligence feeds that track AI-powered malware and emerging threats. Stay informed about new attack techniques and defensive strategies.
- Implement Zero-Trust Architecture: Adopt zero-trust security model that assumes all code and processes are potentially malicious. This approach is essential for defending against adaptive malware.
- Regular Security Testing: Conduct regular penetration testing and red team exercises that simulate AI-powered attacks. This helps identify vulnerabilities and improve defensive capabilities.
FOR INDIVIDUAL USERS & CONSUMERS
- Verify Software Sources: Only download software from official, verified sources. Be cautious of installers with suspicious names or from unknown publishers, especially those that claim to be legitimate software.
- Keep Security Software Updated: Ensure antivirus and security software are updated with the latest behavioral detection capabilities. Traditional signature-based protection may not detect AI-powered malware.
- Monitor System Behavior: Watch for unusual system behavior, such as unexpected network activity, unusual file modifications, or performance degradation, which could indicate malware infection.
- Use Application Whitelisting: Consider using application whitelisting to prevent unauthorized software from executing. This can help prevent AI-powered malware from running even if it successfully evades detection.
- Report Suspicious Activity: Report suspected malware infections or suspicious software to security vendors and the FBI Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3).
FOR GOVERNMENT CONTRACTORS & CRITICAL INFRASTRUCTURE
- Enhanced Monitoring Requirements: Implement enhanced monitoring for AI service usage and API access. Monitor for suspicious patterns that could indicate AI-powered malware operations.
- Federal Compliance: Ensure compliance with federal security requirements for AI-powered threats, including CISA guidance on AI security and behavioral detection.
- Incident Reporting: Establish procedures for reporting AI-powered malware incidents to CISA and other federal agencies within required timeframes.
- Advanced Threat Detection: Deploy advanced threat detection systems capable of identifying AI-powered malware and adaptive attacks. This may require specialized security tools and expertise.
- Continuous Monitoring: Implement 24/7 security operations center capabilities or contract with managed security service providers to continuously monitor for AI-powered threats.
CRITICAL DON’Ts:
- Don’t rely solely on signature-based antivirus – AI-powered malware can evade traditional detection
- Don’t ignore unusual API usage patterns – monitor all AI service access for suspicious activity
- Don’t download software from unverified sources – AI-powered malware often masquerades as legitimate installers
- Don’t disable behavioral detection features – these are essential for identifying adaptive threats
- Don’t assume AI-powered malware is only a future concern – threats are operational now
EMERGENCY RESOURCES & REPORTING
Report Cybersecurity Incidents:
FBI Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3):
- Website: www.ic3.gov
- Emergency Hotline: 1-800-CALL-FBI (1-800-225-5324)
- For: Criminal cyber incidents, malware attacks, AI-powered threats, fraud
CISA Cybersecurity:
- Email: central@cisa.dhs.gov
- 24/7 Operations: 1-888-282-0870
- Website: www.cisa.gov/report
- For: Infrastructure threats, AI-powered malware, vulnerabilities, critical infrastructure protection
US-CERT (Computer Emergency Readiness Team):
- Email: info@us-cert.gov
- For: Technical assistance, vulnerability reporting, AI-powered threat incident response coordination
Google Security:
- For: Reporting misuse of Google AI services, Gemini API abuse, AI-powered malware using Google services
Free Security Tools & Resources:
- CISA Known Exploited Vulnerabilities Catalog – Check for known vulnerabilities in your systems
- CISA Stop Ransomware Guide – Comprehensive ransomware prevention and response guidance
- CISA Shields Up – Cybersecurity readiness resources for organizations
- Have I Been Pwned – Check if your email or password has been compromised in data breaches
RELATED ARTICLES ON CYBERUPDATES365
- AI Phishing Attacks Surge 300%: US CISA Emergency Alert and Protection Strategies
- North Korean Crypto Hackers 2025: Complete Protection Guide
- Deepfake Fraud Protection: FBI Alert Analysis and Prevention Strategies
KEY TAKEAWAYS & FINAL THOUGHTS
The discovery of PROMPTFLUX malware by Google’s Threat Intelligence Group represents a significant milestone in the evolution of AI-powered cyber threats. As the first observed instance of malware that uses AI to dynamically rewrite its own code, PROMPTFLUX signals a fundamental shift from static, signature-based threats to adaptive, AI-powered malware that can evolve in real-time. Official Source: All details in this article are verified through Google Threat Intelligence Group’s official report released November 4, 2025. View Complete Google Cloud Threat Intelligence Blog Report
Critical Points to Remember:
- PROMPTFLUX represents the first observed instance of malware using AI to rewrite its own code in real-time
- Traditional signature-based detection is ineffective against AI-powered adaptive malware
- Organizations must transition to behavioral detection and AI-powered defense systems
- State-sponsored actors and cybercriminals are increasingly abusing AI services across the attack lifecycle
- Google has taken swift action to disable API keys and enhance safeguards, but threat actors will continue to evolve
As AI-powered malware becomes more sophisticated and widespread, organizations must invest in advanced threat detection capabilities and adopt a zero-trust security model. The cybersecurity landscape is evolving rapidly, with AI serving as both a weapon and a shield in the ongoing battle between attackers and defenders.
Staying informed and proactive is essential for defending against emerging AI-powered threats. Organizations that implement comprehensive behavioral detection, monitor API usage, and leverage AI-powered defense systems will be better positioned to identify and respond to adaptive malware like PROMPTFLUX.
Stay Protected with CyberUpdates365
Subscribe for real-time cybersecurity alerts, expert analysis, and actionable security guidance delivered directly to your inbox.
Join 10,000+ cybersecurity professionals and business leaders staying ahead of emerging threats.
Updated on November 6, 2025 by CyberUpdates365 Editorial Team
This is a developing story. CyberUpdates365 is monitoring the situation and will provide updates as new information becomes available from Google Threat Intelligence Group and other security researchers. Follow us on social media for real-time alerts.



Leave a Reply